Blockchain is a system of recording information in a way that makes it difficult or impossible to change, hack, or cheat the system. The simplest way to understand Blockchain is to imagine it as a ledger (or database) for storing transactional information or shared data between millions of computers or connected devices.
In Blockchain, with each transaction was made (send or receive money) — the ledger will automatically update. Each new transaction will be added to a “block”, then put into “chain”.
What makes Blockchain technology becomes revolutionary is that it is secure and decentralized.
By using complex encryption and consensus among computer servers, transactions are performed without a third-party.
Blockchain has the ability to reshape the financial services industry and more than that. Here are 5 things you maybe don’t know about this technology.
1. Blockchain IS NOT Bitcoin

Bitcoin, also known as a “cryptocurrency”, is a type of unregulated digital currency. Bitcoin bypasses government currency controls and helps people to simplify online transactions by getting rid of third-party payment processing intermediaries. Many people believe that blockchain and cryptocurrency bitcoin are the same thing, in reality, they aren’t but they are closely related. Although blockchain provides the underlying technology which helps cryptocurrency exchanges, the potential uses for blockchain are far broader than digital currencies.
2. Blockchain is not just for the finance
Nowadays, Blockchain is not used in financial systems but also continues to expand for other fields such as health data, shipping, power plant data, etc, and will be an increasingly important technology going forward.
Many companies are investing in blockchain technology as part of their infrastructure capabilities like IBM, Microsoft Azure, Amazon (AWS), etc. Blockchain and similar technologies help companies to improve their data security and offer an important step forward in making the important field of the Enterprise of Things safe from hacking and/or hijacking.
3. Blockchain started back 1990
Blockchain technology’s roots can be traced back far further although it has only been effectively used in the past decade. In 1976, a newspaper on New Directions in Cryptography wrote about the idea of a mutual distributed ledger like a field that the blockchain effectively acts. In the 1990s, with a paper entitled How to Time-Stamp a Digital Document, this was later built upon. It would take another few decades, these ideas were viable with the combination of powerful modern computers and the clever implementation with a cryptocurrency.
4. There is more than 1 Blockchain Type
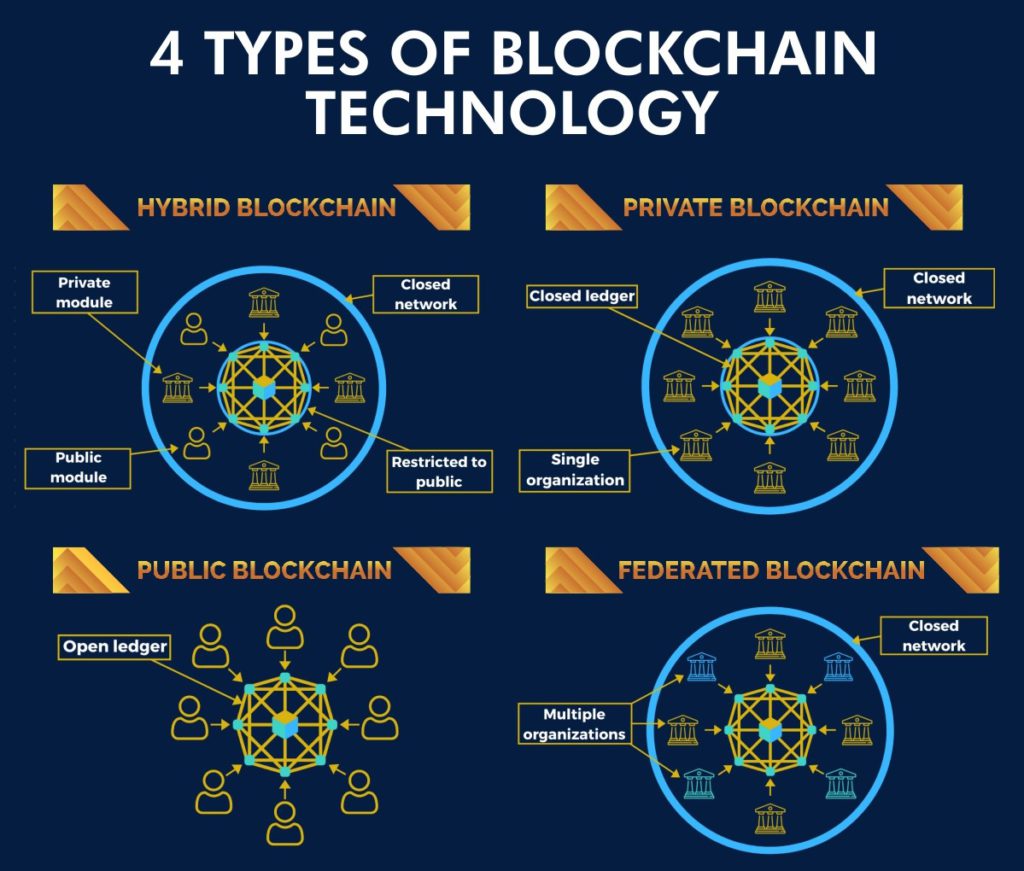
When hearing about blockchain, some people believe that there is only one Blockchain, the reality is there mainly four types:
- Public Blockchain such as Bitcoin, Litecoin: is the blockchain of public, anyone can participate in reading/writing/auditing the blockchain and no one is in charge. In addition to this, these types of blockchain are open and transparent, therefore anyone can review anything at a given point of time on a public blockchain.
- Private Blockchain like Bankchain: is a private property of an individual or an organization. There is an in charge who selectively gives access to read or vice versa or whom to look after of important things such as read/write.
- Consortium or Federated Blockchain, for example r3, EWF: This type of blockchain uses private blockchains in order to remove the sole autonomy which gets vested in just one entity. There is more than one in charge like representative individuals coming together or a group of companies and making decisions for the best benefit of the whole network.
- Hybrid blockchains are blockchains that are controlled by a single organization, but with a level of oversight performed by the public blockchain, which is required to perform certain transaction validations. An example of a hybrid blockchain is IBM Food Trust, which was developed to improve efficiency throughout the whole food supply chain.
5. Blockchain is more than just a Ledger
Blockchain is an innovation in the payments and fintech world. It’s often explained as being a distributed ledger, which is the “true innovation of bitcoin”. This is a half-truth, by itself the ‘chain of blocks’ does not give rise to any benefits of a blockchain system, such as ‘immutability’.
Source: https://medium.com/@adriansoon/5-things-you-dont-know-about-blockchain-bdbc96d67713


